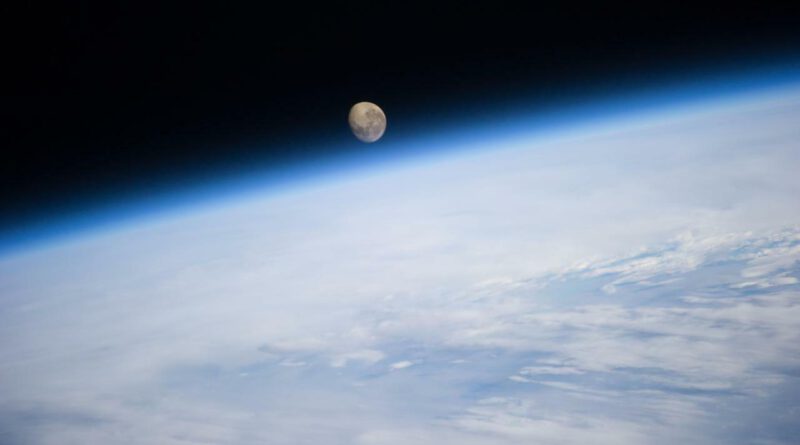
How far is the moon from Earth anyway?

As Earth’s natural satellite, the moon is our planet’s closest space neighbor and companion, joining us for the over 365-day journey around the sun.
But “close” is a relative term in the expanding universe. The moon is about 238,855 miles away, meaning you could fit 30 Earth-size planets in between it and the blue marble, according to NASA.
The distance is always changing, though, because the moon’s orbit around Earth is not a perfect circle — it’s an oval. At its farthest point, the moon is 252,088 miles away from Earth. When the two are closest together, they’re 225,623 miles apart.
And, an interesting piece of trivia if you want to impress friends — or strangers — at a party: The moon is slowly moving away from Earth, getting about an inch farther each year.
The difficult journey to the moon is back at the forefront of space exploration now that NASA, other spacefaring nations, and even commercial players are interested in whether water ice is buried within the dark craters of the moon’s south pole. If the ice could be mined, the water could be used for drinking and making rocket fuel. The latter could turn the moon into something akin to a space gas station.
How long does it take to get to the moon?
How long it takes to get to the moon is an entirely different question, and the answer varies depending on different factors, such as the speed of the spacecraft and its route. Modern rockets and propulsion systems can get to the moon between two-and-a-half and four days.
Some spaceflights to the moon take a more scenic route to save on fuel costs. The Hakuto-R mission, a robotic commercial flight by Japanese company ispace, launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket Dec. 11, 2022. It didn’t reach lunar orbit until March 21, 2023, three months later — the flight was successful, but it failed its ultimate goal of landing on the surface.

Want more science and tech news delivered straight to your inbox? Sign up for Mashable’s Light Speed newsletter today.
Many crewless, robotic spacecraft have flown to the moon, but only 24 people have made the trip, with just half of them walking its surface. The last human to land on the moon was in 1972. That may change soon, as NASA prepares to send astronauts to the lunar south pole through its new Artemis campaign.
NASA selected Christina Hammock Koch, Reid Wiseman, and Victor Glover, and the Canadian Space Agency tapped Jeremy Hansen, for the Artemis II mission, making them the first people to travel into deep space since the final Apollo mission. The flight is scheduled to launch as early as 2024.
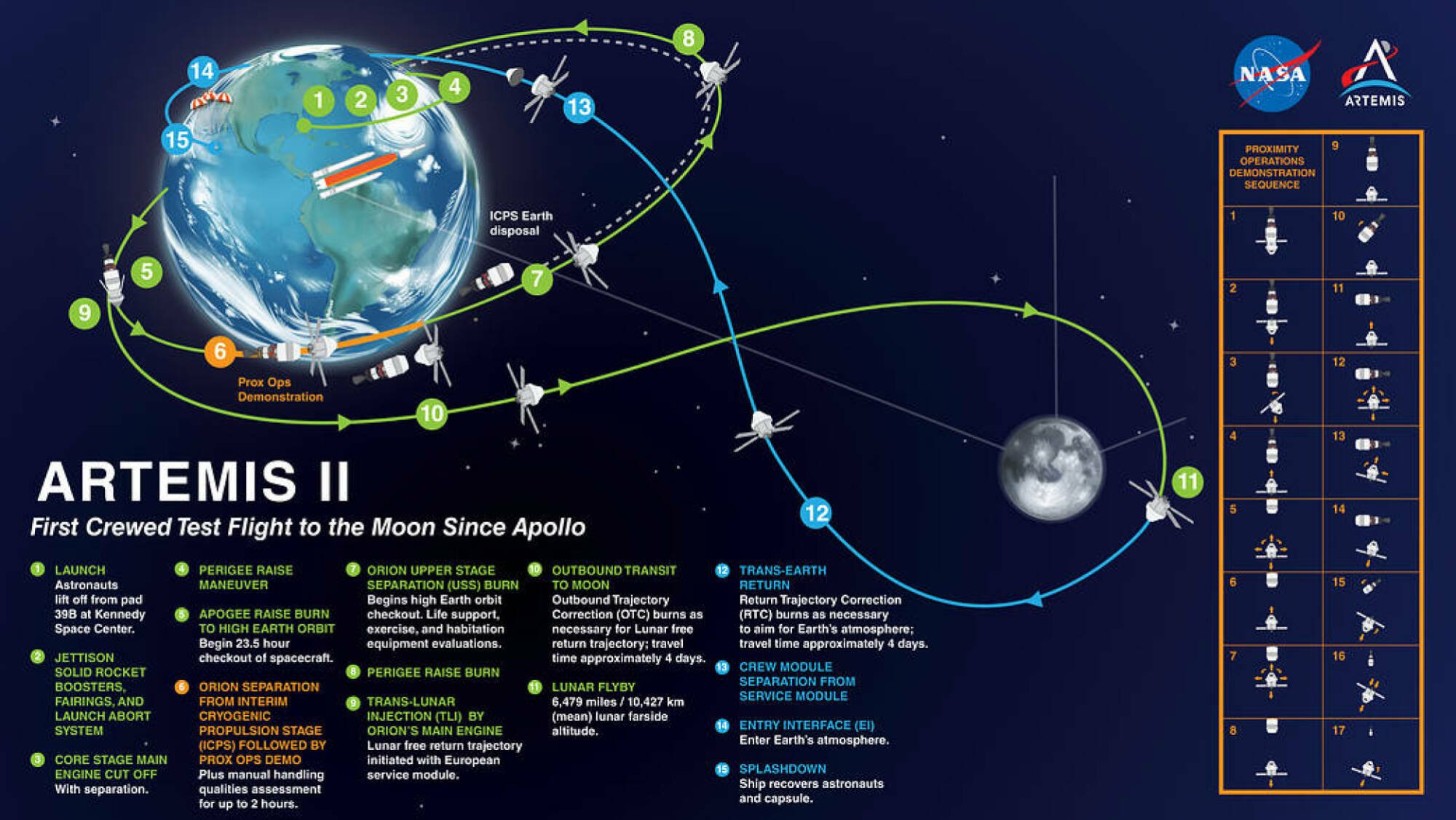
They won’t actually land. Instead, the four crew members will journey 6,400 miles beyond the far side of the moon to test the Orion spacecraft’s life-support systems. Only after the ship has been thoroughly vetted will the U.S. space agency feel confident about using it to send astronauts back for a moonwalk.
If all goes according to plan, NASA will put the first woman and person of color on the moon during the Artemis III mission in 2025 or later.
